HARNESS ASSEMBLY
18. March 2020
CRASH SYSTEMS
20. March 2020PACS
- Client
- Kayser-Threde GmbH (now OHB)
- Links
- Max Planck Institute for extraterrestrial Physics
esa
PACS
(Photodetector Array Camera & Spectrometer)
The infrared spectrometer and photometer PACS is one of three scientific instruments for the ESA satellite telescope Herschel.
The science satellite Herschel was launched in 2007. As one of the coldest points in space - the detectors of the cryogenic measuring system PACS are operated close to absolute zero - it will help to clarify fundamental questions in the development of space.
Herschel will be the world's largest space telescope when it is launched. Information about star formation from interstellar gas and dust, identification and characterization of black holes, formation of galaxies and their behavior in collisions, as well as the possibility of obtaining information about processes of planet formation, are just some of the astronomical research areas for which PACS will be used.
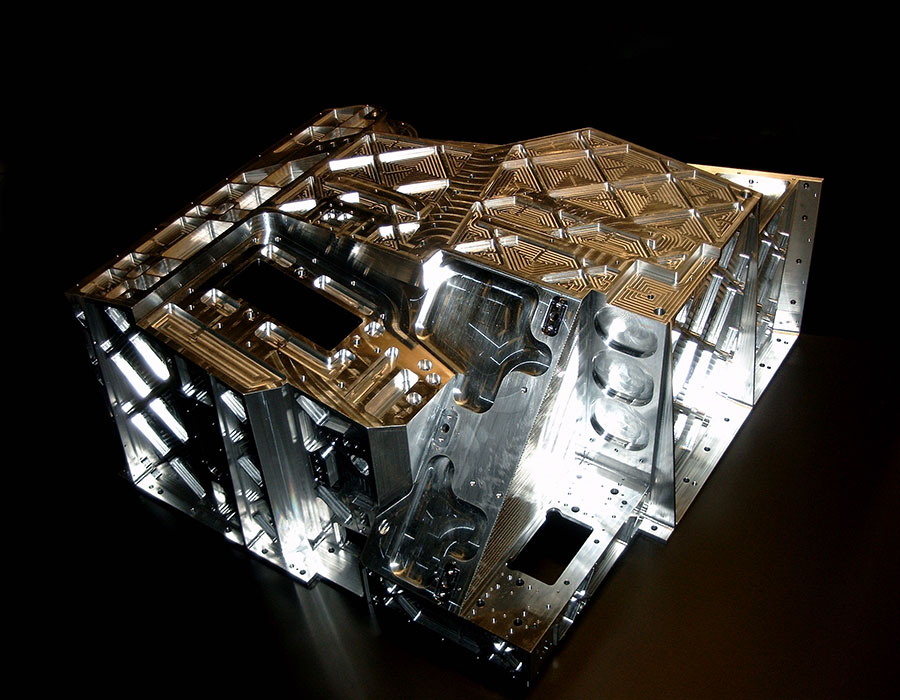
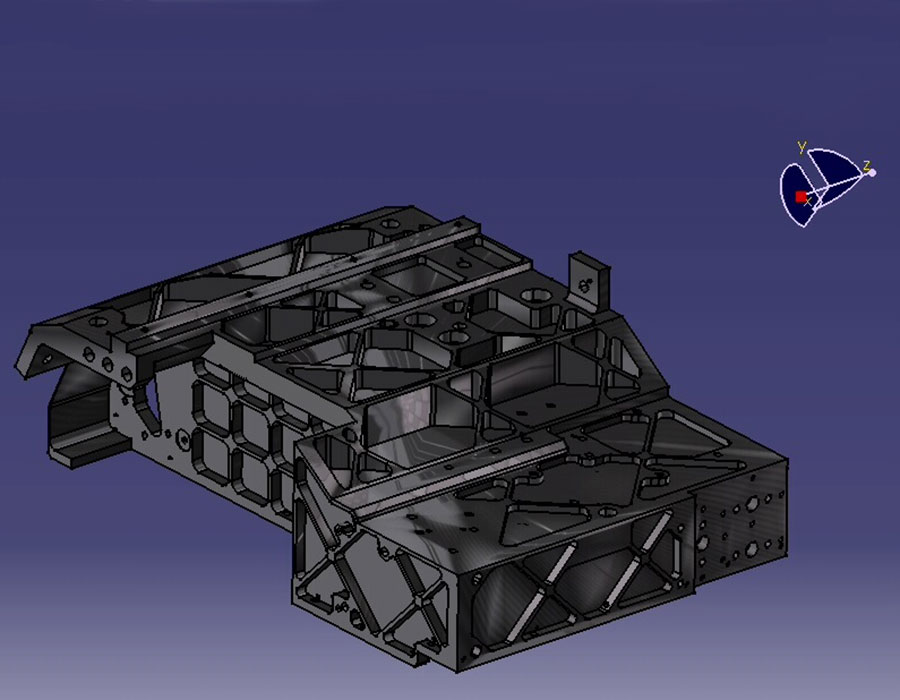
The highly sensitive measuring instrument consists of a complicated, three-dimensional opto-mechanical bench with more than 50 precisely adjustable mirror and four detector units. The particular fascination of this mission lies in its unprecedented ability to detect long-wave infrared light from the early stages of the universe.
The scientific instrument is planned by 14 European institutes and universities under the leadership of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE) in Garching. The development of the optomechanics as well as the system integration and verification of the high-tech instrument was carried out at Kayser-Threde, Munich.
Our contribution
Already during the first studies, we designed the housing around the mirrors and detectors and adapted it again and again to the changing optics in order to enable up-to-date thermal and structural analyses at the same time.